What is a Pump?
A pump is a mechanical device that transfers different fluids from one location to another by applying mechanical action. The pump transfers the mechanical energy of the prime mover or other external energy to the liquid, increasing the energy of the liquid.
Pumps are mainly used to transport liquids such as water, oil, acid and alkali liquids, emulsions, suspensions, and liquid metals. They can also transport liquid-gas mixtures and liquids containing suspended solids.
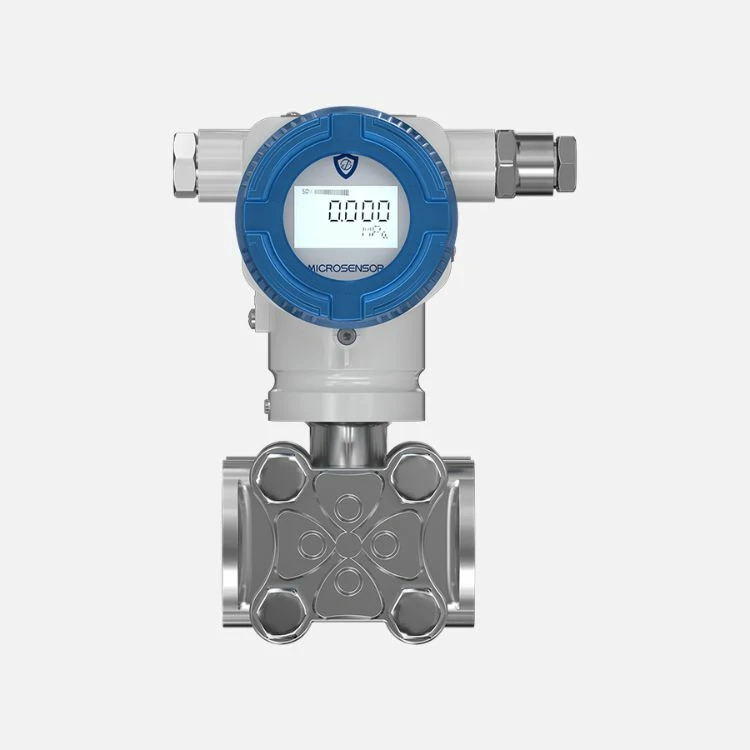
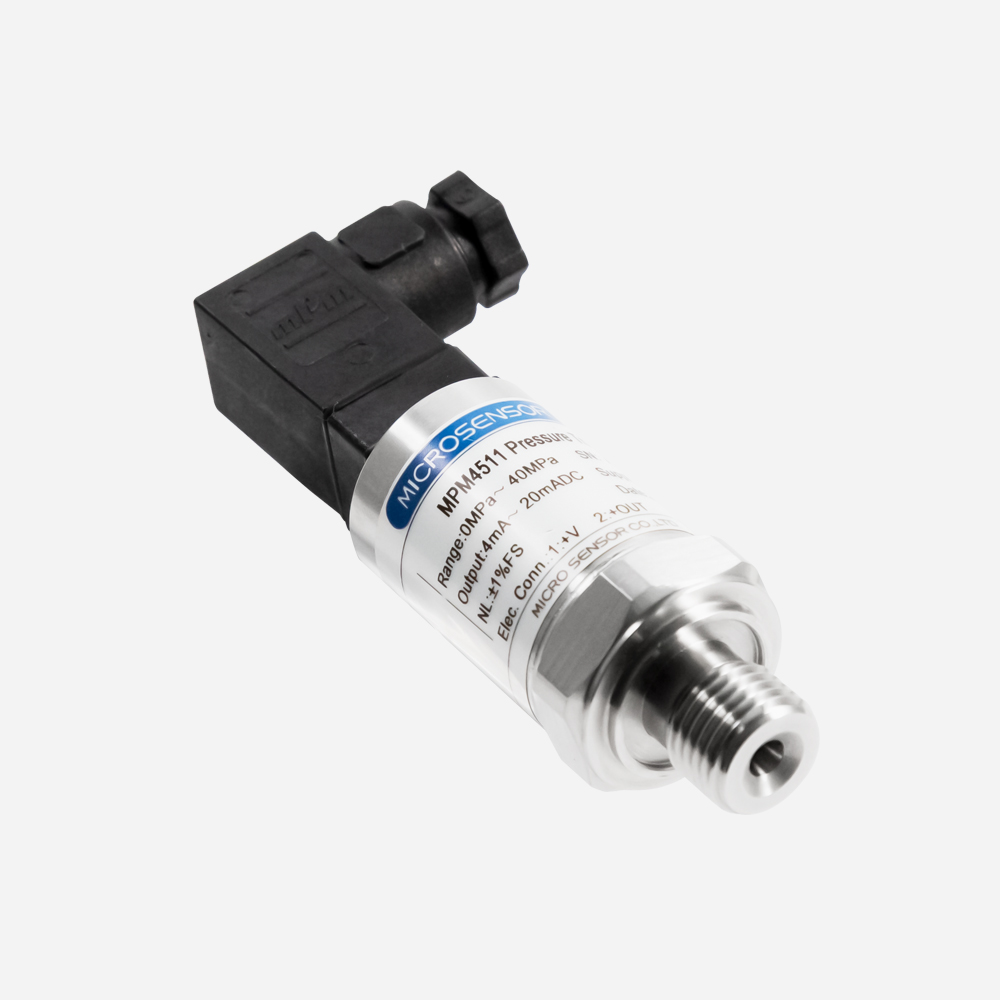
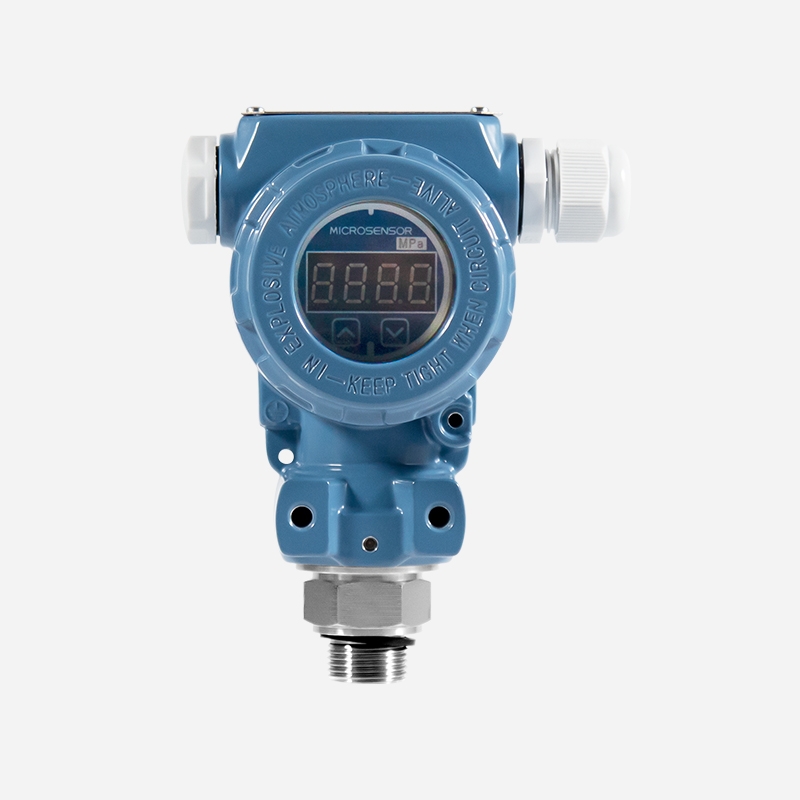
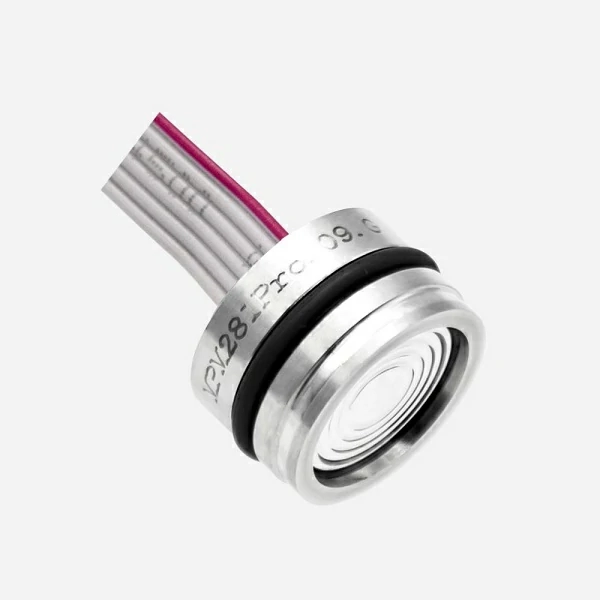
How Does Pressure Transmitter Work for Pumps?
In a variable speed or constant pressure pump system, a pressure transmitter converts the fluid pressure in the pipe into an electrical signal. Then, the signal is sent to the variable frequency drive (VFD) that powers the system. The VFD uses this signal to increase or decrease the pump speed to match the required pressure range of the system. The main purpose of a pressure sensor is to maintain a constant fluid pressure by acting as a signaling device for the VFD.
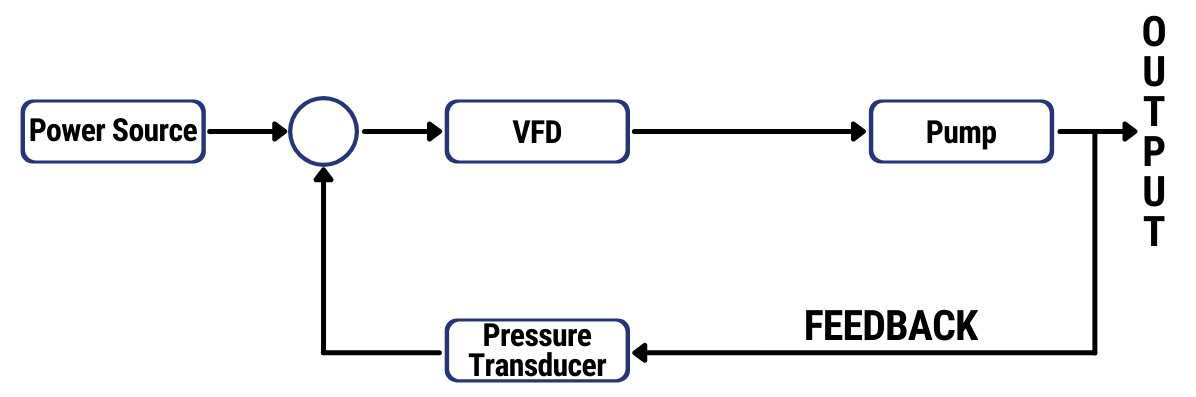
Why Do Pumps Need Pressure Transducers?
• Pressure transducers monitor the pressure in the water pipes in real-time to ensure a steady water flow supply. They maintain the water pressure within a preset safety range.
• Pressure transducers help optimize the speed of the pump, thereby greatly reducing the power consumption during operation. Pump systems equipped with pressure sensors are much more efficient than traditional pump devices.
• Pressure transducers reduce mechanical stress when starting and shutting down. Then, the pressure on the internal components of the pump is greatly reduced during operation. The pump system will have a longer service life.
Main Application of Pressure Transmitters in the Pump Industry

• Water Lift Systems: Traditional gravity-fed water systems with water towers cannot apply the necessary pressure. Pumps are ready to lift water to the higher location. Pressure transducers in pumping systems measure fluid pressure to keep standard operation.
• Clean Water Systems: Water is commonly moved from one treatment facility to another by a pump system via a pipeline. Pressure instruments feedback signal to a VFD on the pump which ensures reliable transportation.
• Sewage Pumping Systems: Pumps deliver sewage to treatment plants. Inlet and outlet pressure help the pump control whether the flow rate needs to be increased or decreased.
Proper Placement of Pressure Sensors in Pump Systems
• Choose Installation Location: Pressure monitoring devices should be installed at the following locations: ① Inlet and outlet points of the pump system provide a comprehensive understanding of the pressure changes in the entire system; ② Key points where pressure fluctuations may have a significant impact.
• Avoid Vibration and Heat Sources: Areas with excessive vibration or heat sources can affect the accuracy and reliability of pressure readings.
• Consider Pipeline Characteristics: When determining the location of the pressure monitoring device, pipeline characteristics such as diameter and material should be considered. Certain pipeline configurations may affect pressure readings, and proper consideration can help reduce potential errors.
Proper installation ensures the effectiveness of pressure monitoring in the pump system.
































 Copyright © 2025 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD
Copyright © 2025 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD



